Diesel Engine
The diesel engine was first patented in 1892 by Rudolph Diesel.8
The diesel is similar to the four stroke, but uses a different method to ignite the fuel.
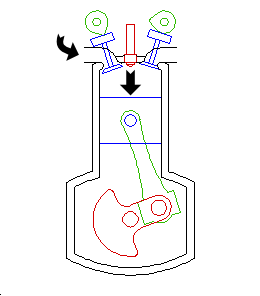
Intake
The intake valve opens, and fresh air (containing no fuel), is drawn into the cylinder.
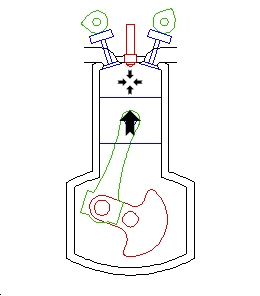
Compression
As the piston rises, the air is compressed, causing its temperature to rise. At the end of the compression stroke, the air is hot enough to ignite fuel.
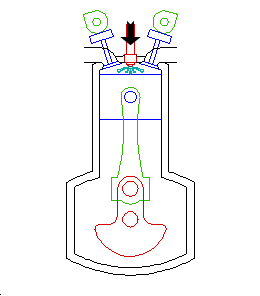
Injection
Near the top of the compression stroke, the fuel injector drives fuel into the cylinder. The fuel immediately ignites upon contact with the hot compressed air.
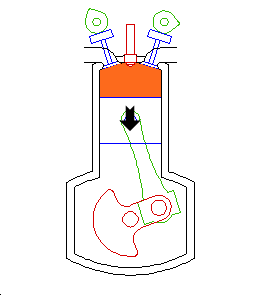
Power
As the fuel burns, the gas in the cylinder heats and expands, driving the piston.
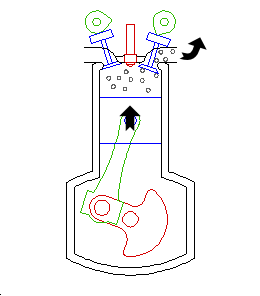
Exhaust
The exhaust valve opens, and the exhaust is driven out of the cylinder.
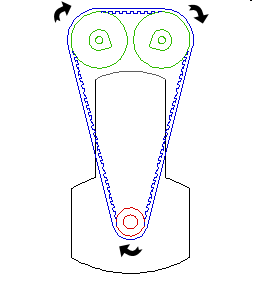
Valve detail
The valves are operated by a variety of mechanisms on diesel and four stroke engines. The engine illustrated here features dual overhead camshafts, sometimes abbreviated DOHC. These are usually driven by a chain or cog belt as shown here.
With his first practical engine in 1897, “Diesel proved to the world that his was the most efficient engine ever built.”8 Diesels are still among the most energy efficient engines available. They are widely used in large trucks, boats, earthmoving machinery, etc.

 Follow
Follow Befriend
Befriend Subscribe
Subscribe